A reliable Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) system is essential for protecting your electronic devices from power interruptions, surges, and spikes. Calculating the power requirements for your UPS system ensures that you choose a unit capable of supporting your equipment during outages. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you determine the power requirements for your UPS system.
List All the Devices
Start by listing all the devices you intend to connect to the UPS. This can include computers, monitors, servers, network equipment, and any other critical electronic devices.
Determine the Power Consumption of Each Device
Check the power consumption (usually in watts) for each device. This information can typically be found on the device's power adapter, label, or in the user manual. If the power consumption is listed in amperes (A), you can convert it to watts (W) using the following formula:
Watts= Volts × Amperes
For most devices in the US, the voltage is 120V.
Calculate the Total Power Consumption
Add up the power consumption of all the devices to get the total power requirement. This is the minimum power rating your UPS should have.
Consider the Power Factor
Most UPS systems are rated with a power factor, usually between 0.6 and 0.9. The power factor is the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt-amperes). To ensure your UPS can handle the load, divide the total power consumption by the power factor:
Required VA = Power Factor Total / Power Consumption (W)
For example, if your total power consumption is 800W and your UPS has a power factor of 0.8:
Required VA= 800W/0.8=1000VA
Factor in Future Expansion
It's wise to consider future expansion when selecting a UPS. Add an extra margin (usually 20-25%) to your calculated power requirement to accommodate additional devices or increased power consumption in the future.
Total Required VA= Required VA x 1.25
Using the previous example:
Total Required VA= 1000VA x 1.25= 1250VA
Determine the Required Runtime
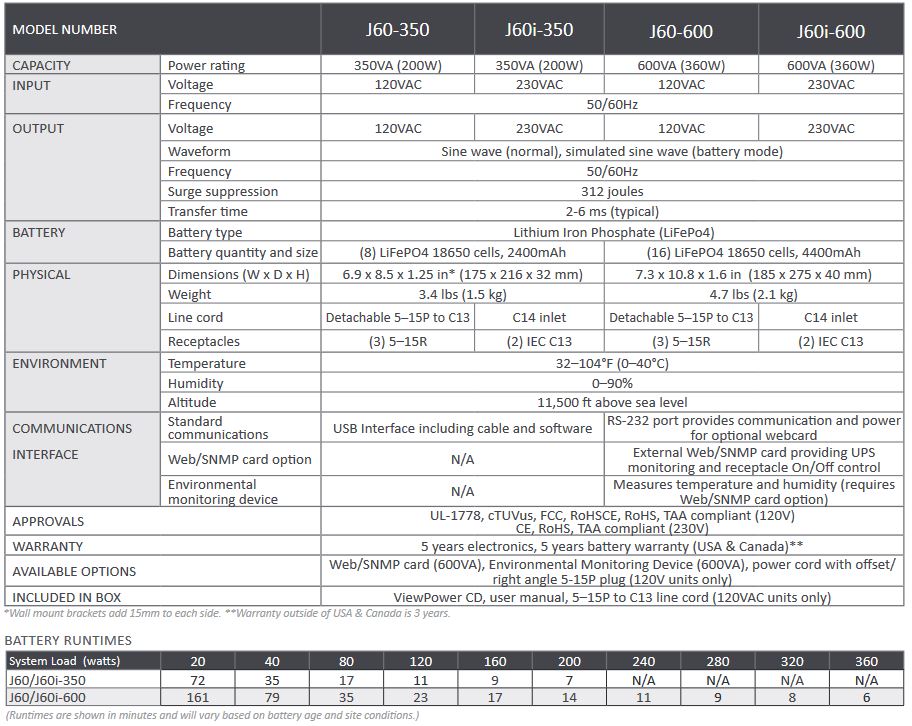
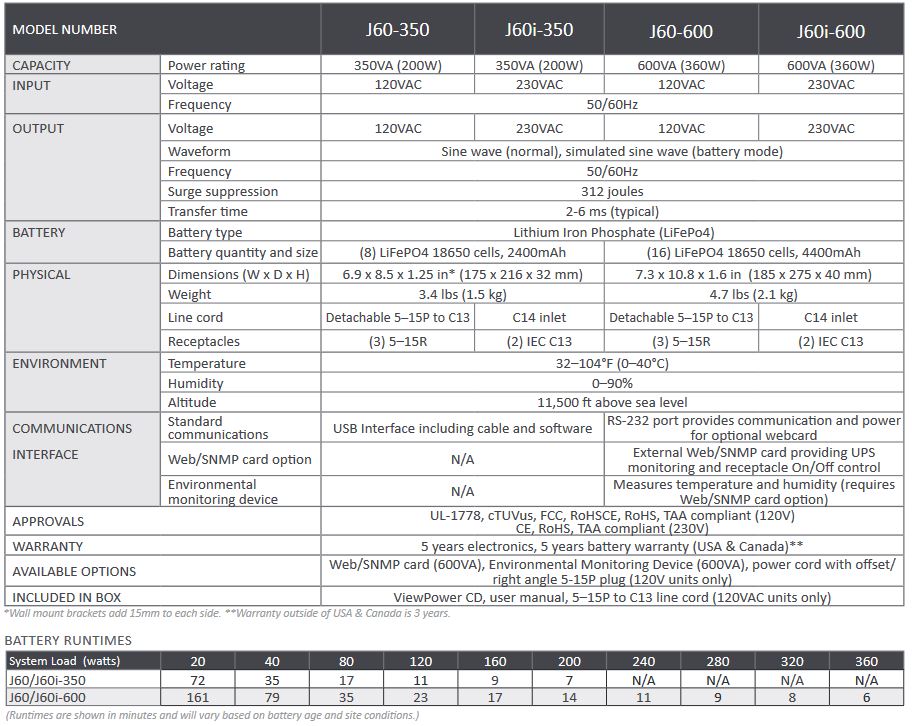
Decide how long you need your devices to run during a power outage. UPS systems are rated for different runtimes at various loads. Check the manufacturer's specifications for runtime charts that show how long the UPS can support your load.
Select the Appropriate UPS
With all the information gathered, you can now select a UPS that meets your power and runtime requirements. Look for a UPS with a VA rating that matches or exceeds your total required VA and offers the desired runtime for your load.
Check for Additional Features
Consider any additional features you may need, such as:
- Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR): Protects against voltage fluctuations.
- Surge Protection: Shields devices from power surges.
- Management Software: Allows for monitoring and managing the UPS.
- Expandability: Some UPS systems allow for additional battery packs to extend runtime.
Conclusion
Calculating the power requirements for your UPS system is a crucial step in ensuring your electronic devices remain protected during power interruptions. By following these steps, you can accurately determine the power needs of your equipment and choose a UPS system that provides reliable backup power and peace of mind. Remember to account for future growth and consider additional features that may benefit your specific setup.